Seguridad y soberanía en el Ártico: El papel de las estructuras modulares

Ali Salman es Director de Marketing Estratégico de Crecimiento y Ventas de Northgate Industries.
El Ártico, antaño considerado una región remota y en gran medida inaccesible, se ha convertido en un punto crítico de interés geopolítico. A medida que el cambio climático acelera el deshielo, el Ártico está revelando nuevas rutas de navegación y vastos recursos naturales sin explotar, lo que lo convierte en un foco de interés estratégico mundial. Este artículo profundiza en la dinámica geopolítica de la seguridad del Ártico, especialmente para Canadá y la OTAN, al tiempo que explora cómo las estructuras modulares pueden desempeñar un papel fundamental en la mejora de la seguridad y la soberanía en esta región cada vez más disputada.
La importancia estratégica del Ártico
Según el Servicio Geológico de Estados Unidos (USGS), el Ártico alberga aproximadamente el 13% de las reservas mundiales de petróleo y el 30% de las de gas natural por descubrir. El deshielo ha hecho más accesibles estos recursos, despertando el interés y la competencia de los Estados árticos y no árticos por igual. Para Canadá, el Ártico no es sólo una zona rica en recursos, sino también un componente esencial de su soberanía nacional. El marco político del gobierno canadiense para el Ártico subraya la importancia de afirmar la soberanía y mantener una fuerte presencia en la región para salvaguardar sus intereses nacionales.
La OTAN también ha reconocido la creciente importancia del Ártico en su concepto estratégico. La reciente atención prestada por la Alianza al Ártico responde a las crecientes actividades militares de Rusia, que ha estado reforzando su presencia en el Ártico con nuevas bases, rompehielos y sistemas avanzados de armamento. Las ambiciones de Rusia en el Ártico, especialmente su control sobre la Ruta Marítima Septentrional (NSR), plantean importantes retos para la seguridad de la región, suscitando la preocupación de los miembros de la OTAN ante la posibilidad de un conflicto.
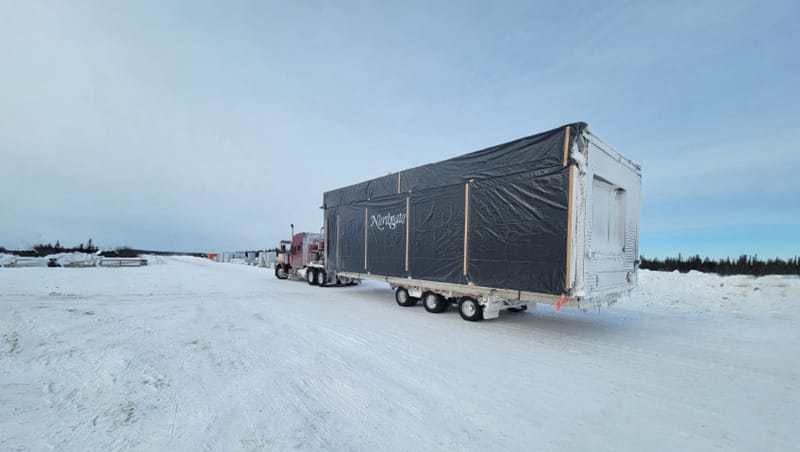

Northgate Industries transporta unidades modulares por terreno ártico.
China, aunque no es un Estado ártico, también ha manifestado su interés por el Ártico, considerándose un "Estado cercano al Ártico" y tratando de ampliar su influencia mediante iniciativas como la Ruta de la Seda Polar. La creciente presencia de China en el Ártico, que incluye inversiones en infraestructuras y asociaciones con Estados árticos, ha añadido otro nivel de complejidad a la dinámica de seguridad de la región.
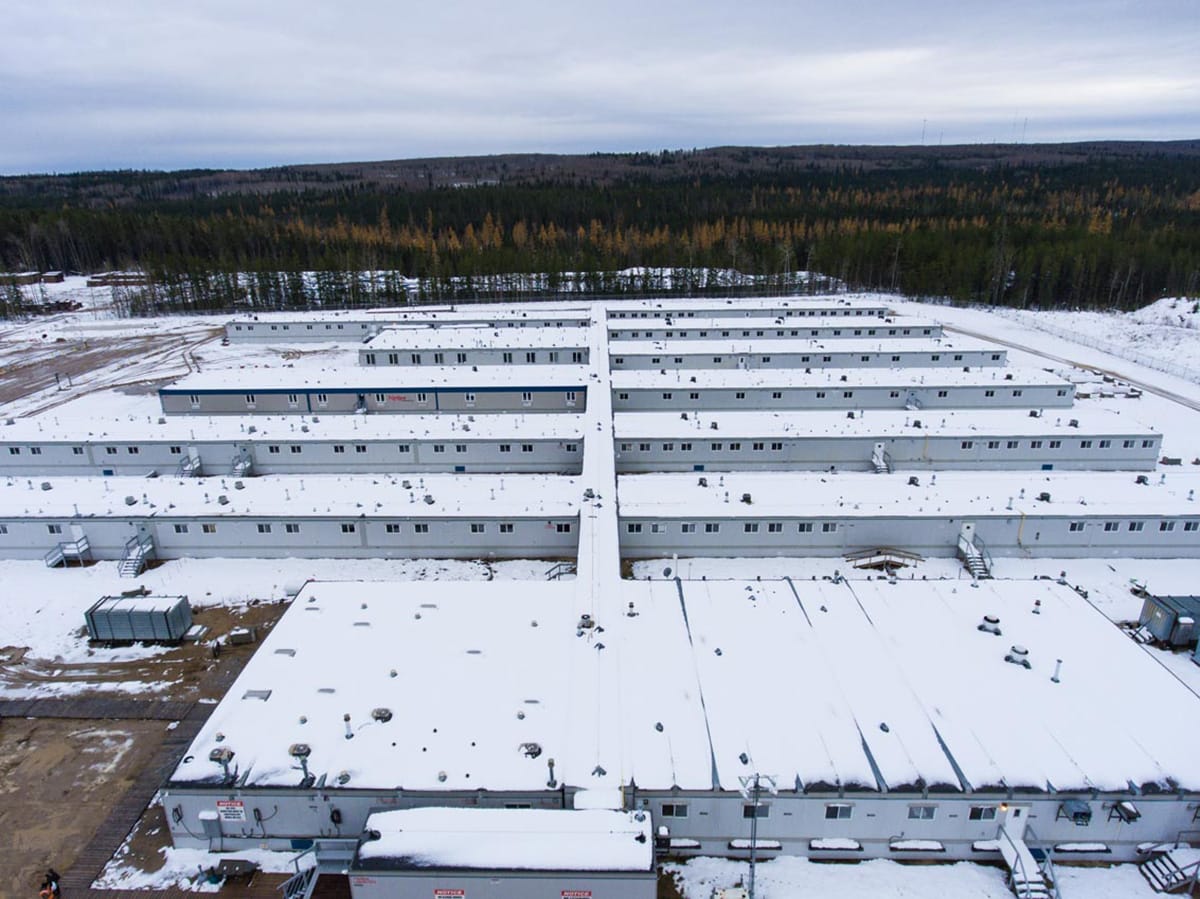

Durante el ejercicio Trident Juncture 2018, la OTAN empleó unidades modulares para proporcionar apoyo logístico en el difícil entorno del Ártico noruego.
La importancia estratégica del Ártico
Aunque los retos geopolíticos del Ártico son inmensos, el entorno físico de la región presenta su propio conjunto de obstáculos. La dureza del clima, las condiciones meteorológicas extremas y las dificultades logísticas dificultan el establecimiento y mantenimiento de una presencia sostenida en el Ártico. En este contexto, las estructuras modulares ofrecen una solución práctica y eficaz, proporcionando la flexibilidad, rapidez y resistencia necesarias para las operaciones en un entorno tan remoto y hostil.
Despliegue rápido y flexibilidad
Las estructuras modulares son prefabricadas y pueden desplegarse rápidamente en lugares remotos, una ventaja crucial en el Ártico, donde la construcción tradicional se ve obstaculizada por el clima extremo y las temporadas de construcción limitadas. Northgate Modular, líder en construcción modular, ha demostrado que las unidades modulares pueden montarse entre un 30% y un 50% más rápido que los métodos tradicionales, lo que las hace ideales para establecer rápidamente una presencia en el Ártico.
Escalabilidad y adaptabilidad
Las estructuras modulares son intrínsecamente escalables, lo que permite la ampliación gradual de las instalaciones según las necesidades. Esta flexibilidad es especialmente beneficiosa para las operaciones militares y de seguridad, en las que el tamaño y el alcance de las misiones pueden cambiar rápidamente. La capacidad de reconfigurar o reubicar unidades modulares con relativa facilidad garantiza que las operaciones puedan adaptarse a las cambiantes condiciones geopolíticas y medioambientales.
Sostenibilidad y eficiencia
El entorno ártico exige prácticas sostenibles, y las estructuras modulares pueden diseñarse con sistemas energéticamente eficientes que reduzcan la huella de carbono de las operaciones. El uso de paneles aislantes y fuentes de energía renovables puede reducir significativamente los costes de calefacción, un factor importante en el Ártico. Según el Arctic Institute, estos diseños energéticamente eficientes pueden reducir el consumo de energía hasta un 40%, lo que hace que las estructuras modulares sean viables tanto desde el punto de vista económico como medioambiental.
Relación coste-eficacia
El ahorro de costes asociado a la construcción modular es sustancial, especialmente en el Ártico, donde los retos logísticos del transporte de materiales y mano de obra pueden disparar los costes. Según un estudio de McKinsey & Company, la construcción modular puede reducir los costes hasta un 20% en comparación con los métodos tradicionales. Este ahorro es especialmente importante para los organismos militares y de seguridad que operan en el Ártico, donde los presupuestos suelen verse limitados por los elevados costes de logística e infraestructura.
Casos prácticos: Estructuras modulares en acción
Fuerzas Armadas Canadienses (CAF)
Las Fuerzas Armadas canadienses han utilizado estructuras modulares en varias operaciones en el Ártico, demostrando sus ventajas prácticas. La instalación naval de Nanisivik, en la isla de Baffin, es un ejemplo clave. Esta instalación, que sirve de apoyo a las operaciones de la Marina Real Canadiense en el Ártico, se construyó utilizando métodos modulares, lo que permitió un despliegue rápido y garantizó que la estructura pudiera soportar las duras condiciones del Ártico. La instalación es un centro logístico esencial que permite a Canadá mantener una presencia continua en la región.

Operaciones de la OTAN
La OTAN también ha reconocido el potencial de las estructuras modulares para mejorar sus capacidades operativas en el Ártico. Durante el ejercicio Trident Juncture 2018, la OTAN empleó unidades modulares para proporcionar apoyo logístico en el desafiante entorno ártico noruego. Este ejercicio puso de relieve la adaptabilidad y resistencia de la construcción modular, mostrando su valor para apoyar los objetivos estratégicos de la OTAN en la región.
Agencias de seguridad
Más allá de las aplicaciones militares, las estructuras modulares son inestimables para otros organismos de seguridad encargados de vigilar y responder a las amenazas en el Ártico. La Guardia Costera canadiense, por ejemplo, ha utilizado unidades modulares para apoyar las operaciones de búsqueda y rescate en todo el Ártico. Estas estructuras proporcionan refugios fiables y de despliegue rápido, garantizando que el personal disponga de la infraestructura necesaria para responder eficazmente a las emergencias.
Implicaciones geopolíticas de la seguridad en el Ártico
El Ártico se está convirtiendo en una región cada vez más disputada, con importantes implicaciones para la seguridad mundial. El creciente interés de Rusia y China, combinado con los vastos recursos naturales y las rutas marítimas estratégicas de la región, ha transformado el Ártico en un posible foco de conflictos internacionales. Para Canadá y la OTAN el reto consiste en desarrollar una estrategia de seguridad que pueda contrarrestar eficazmente estas amenazas manteniendo al mismo tiempo la estabilidad en la región.
El papel de las estructuras modulares en esta estrategia está claro: proporcionan la infraestructura necesaria para establecer y mantener una presencia en el Ártico. Sin embargo, las estructuras modulares son sólo un componente de un marco de seguridad más amplio que debe incluir también la preparación militar, el compromiso diplomático y la cooperación internacional.
A medida que el Ártico siga calentándose y sus recursos se hagan más accesibles, la necesidad de un enfoque coordinado y global de la seguridad en la región no hará sino aumentar.
Las estructuras modulares, con su capacidad para desplegarse rápidamente y adaptarse a condiciones cambiantes, constituirán un elemento clave de esta estrategia, permitiendo a Canadá y a la OTAN mantener una presencia fuerte y adaptable en el Ártico.
Conclusión
El cambiante panorama geopolítico del Ártico exige soluciones innovadoras para los complejos retos de seguridad. Para Canadá y la OTAN el mantenimiento de la soberanía y la seguridad en el Ártico no es sólo una cuestión de interés nacional sino un componente esencial de la estabilidad mundial.
Más de Modular Advantage
How Stack Modular Is Using AI to De-Risk Mid- to High-Rise Modular Construction
Artificial intelligence is no longer a future concept in modular construction—it is already reshaping how complex buildings are evaluated, designed, and delivered.
Preparándonos para el mundo modular de 2026
El Modular Building Institute (MBI) vuelve a celebrar en abril en Las Vegas su conferencia y feria comercial mundial World of Modular (WOM), que ofrece algunas de las mejores oportunidades del sector para establecer contactos, desarrollar negocios y formarse.
El nuevo edificio modular de apartamentos en Abu Dhabi apunta hacia el futuro de la construcción multifamiliar.
Eagle Hills International Properties chose the BROAD Holon Building for a 16-story market rate apartment building in Zayed City, a central business district of Abu Dhabi. The project highlights the potential of the Holon system of volumetric modular construction to accelerate housing delivery.
MBI anuncia el primer programa de aprendizaje industrial en colaboración con el Marshall Advanced Manufacturing Center
MBI acordó recientemente asociarse con Marshall Advanced Manufacturing Center (MAMC) para ofrecer programas de aprendizaje auténticos y aprobados por el Departamento de Trabajo de los Estados Unidos (USDOL) para la industria.
AoRa Development aspira a construir el primer edificio triple net zero de Nueva York utilizando métodos modulares.
Cada vez más ciudades están financiando nuevos proyectos de infraestructura, siempre y cuando cumplan con los requisitos de sostenibilidad. Así es como los módulos pueden encajar en este panorama, gracias a su menor producción de residuos.
Desarrolladores y diseñadores: lecciones aprendidas con el diseño modular
La construcción modular resulta atractiva para muchos promotores porque las obras y la construcción de los módulos pueden realizarse simultáneamente, lo que acorta los plazos y reduce los costes adicionales.
UTILE: Acelerando la construcción modular
En Quebec, UTILE está liderando la creación de edificios modulares asequibles para ayudar a reducir la escasez de viviendas para estudiantes. Durante el proceso, la empresa descubrió lo que se necesita para que la transición a la construcción modular sea un éxito.
Sobha Modular enseña a los desarrolladores a pensar como fabricantes
Con su fábrica de 250 000 metros cuadrados en los Emiratos Árabes Unidos, Sobha Modular está llevando sus cuartos de baño modulares de alta gama a residencias de lujo en Dubái, al tiempo que desarrolla proyectos modulares para Estados Unidos y Australia.
RoadMasters: Por qué la planificación temprana del transporte es fundamental en la construcción modular
En la construcción modular, el transporte suele denominarse «el eslabón perdido». Aunque rara vez detiene un proyecto por completo, una mala planificación puede provocar costosos retrasos, cambios de ruta y sobrecostes.
Cómo gestionar los riesgos en el sector inmobiliario comercial y la construcción modular: perspectivas de un veterano con 44 años de experiencia en el sector.
Los proyectos modulares implican la fabricación, el transporte y el montaje in situ. Los promotores deben comprender exactamente cuáles son sus responsabilidades y cuáles son las tareas que subcontratan. Los asesores de riesgos deben investigar a los contratistas, subcontratistas y consultores de diseño y construcción del promotor, especialmente al fabricante modular.